Oracle Exam
Q: 1)
Evaluate the SQL statement:
TRUNCATE TABLE DEPT;
Which three are true about the SQL statement? (Choose three.)
A. It releases the storage space used by the table.
B. It does not release the storage space used by the table.
C. You can roll back the deletion of rows after the statement executes.
D. You can NOT roll back the deletion of rows after the statement executes.
E. An attempt to use DESCRIBE on the DEPT table after the TRUNCATE statement executes will
display an error.
F. You must be the owner of the table or have DELETE ANY TABLE system privileges to truncate
the DEPT table
Answer:A,D,F
Q:2)
QUESTION NO: 2
You need to design a student registration database that contains several tables storing academic
information.
The STUDENTS table stores information about a student. The STUDENT_GRADES table stores information about the student's grades. Both of the tables have a column named STUDENT_ID.
The STUDENT_ID column in the STUDENTS table is a primary key.
You need to create a foreign key on the STUDENT_ID column of the STUDENT_GRADES table
that points to the STUDENT_ID column of the STUDENTS table. Which statement creates the
foreign key?
A. CREATE TABLE student_grades (student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), CONSTRAINT student_id_fk REFERENCES (student_id) FOREIGN KEY
students(student_id));
B. CREATE TABLE student_grades(student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), student_id_fk FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(student_id));
C. CREATE TABLE student_grades(student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(student_id));
D. CREATE TABLE student_grades(student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), CONSTRAINT student_id_fk FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES
students(student_id));
Answer: D
Q:3)
Here is the structure and data of the CUST_TRANS table:
Dates are stored in the default date format dd-mm-rr in the CUST_TRANS table.
Which three SQL statements would execute successfully? (Choose three.)
A. SELECT transdate + '10' FROM cust_trans;
B. SELECT * FROM cust_trans WHERE transdate = '01-01-07';
C. SELECT transamt FROM cust_trans WHERE custno > '11';
D. SELECT * FROM cust_trans WHERE transdate='01-JANUARY-07';
E. SELECT custno + 'A' FROM cust_trans WHERE transamt > 2000;
Answer: A,C,D
Q:4)
See the Exhibit and examine the structure and data in the INVOICE table:
Which two SQL statements would executes successfully? (Choose two.)
A. SELECT MAX(inv_date),MIN(cust_id) FROM invoice;
B. SELECT MAX(AVG(SYSDATE - inv_date)) FROM invoice;
C. SELECT (AVG(inv_date) FROM invoice;
D. SELECT AVG(inv_date - SYSDATE),AVG(inv_amt) FROM invoice;
Answer: A,D
Q:5)
QUESTION NO: 5
Which three statements are true regarding sub queries? (Choose three.)
A. Multiple columns or expressions can be compared between the main query and sub query
B. Main query and sub query can get data from different tables
C. Sub queries can contain GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses
D. Main query and sub query must get data from the same tables
E. Sub queries can contain ORDER BY but not the GROUP BY clause
F. Only one column or expression can be compared between the main query and subqeury
Answer: A,B,C
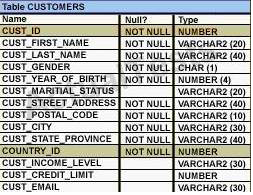
Q:6)See the Exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS table:
Using the CUSTOMERS table, you need to generate a report that shown the average credit limit
for customers in WASHINGTON and NEW YORK.
Which SQL statement would produce the required result?
A.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK')
GROUP BY cust_credit_limit, cust_city;
B.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK')
GROUP BY cust_city,cust_credit_limit;
C.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK')
GROUP BY cust_city;
D.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(NVL(cust_credit_limit,0))
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK');
Answer: C
Q:7)
Evaluate these two SQL statements:
SELECT last_name, salary, hire_date FROM EMPLOYEES ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT last_name, salary, hire_date FROM EMPLOYEES ORDER BY 2 DESC;
What is true about them?
A. The two statements produce identical results.
B. The second statement returns a syntax error.
C. There is no need to specify DESC because the results are sorted in descending order by
default.
D. The two statements can be made to produce identical results by adding a column alias for the
salary column in the second SQL statement.
Answer: A
Q:8)
Where can sub queries be used? (Choose all that apply)
A. field names in the SELECT statement
B. the FROM clause in the SELECT statement
C. the HAVING clause in the SELECT statement
D. the GROUP BY clause in the SELECT statement
E. the WHERE clause in only the SELECT statement
F. the WHERE clause in SELECT as well as all DML statements
Answer: A,B,C,F
Q:9)
Which three SQL statements would display the value 1890.55 as $1,890.55? (Choose three.)
A.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$99G999D00')
FROM DUAL;
B.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$9,999V99')
FROM DUAL;
C.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$0G000D00')
FROM DUAL;
D.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$99G999D99')
FROM DUAL;
E.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$9,999D99')
FROM DUAL;
Answer: A,C,D
Q:10)
Evaluate the following SQL statement:
Which statement is true regarding the outcome of the above query?
A. It produces an error because the ORDER BY clause should appear only at the end of a
compound query-that is, with the last SELECT statement
B. It executes successfully and displays rows in the descending order of PROMO_CATEGORY
C. It executes successfully but ignores the ORDER BY clause because it is not located at the end
of the compound statement
D. It produces an error because positional notation cannot be used in the ORDER BY clause with
SET operators
Answer: A
Q: 11)
Which statement correctly describes SQL and /SQL*Plus?
A. Both SQL and /SQL*plus allow manipulation of values in the database.
B. /SQL*Plus recognizes SQL statements and sends them to the server; SQL is the Oracle
proprietary interface for executing SQL statements.
C. /SQL*Plus is a language for communicating with the Oracle server to access data; SQL
recognizes SQL statements and sends them to the server.
D. SQL manipulates data and table definitions in the database; /SQL*Plus does not allow
manipulation of values in the database.
Answer: A
Q: 12)
Which four are types of functions available in SQL? (Choose 4)
A. string
B. character
C. integer
D. calendar
E. numeric
F. translation
G. date
H. conversion
Answer: B,E,G,H
Q:13)
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES and NEW_EMPLOYEES tables:
A.
MERGE INTO new_employees c
USING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT
value
S(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
B.
MERGE new_employees c
USING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN EXISTS THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT
valueS(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
Oracle 1z0-051 Exam
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 11
C.
MERGE INTO new_employees cUSING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN EXISTS THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT
value
S(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
D.MERGE new_employees c
FROM employees e ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE
MERGE INTO new_employees cUSING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN EXISTS THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT
value
S(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
E.MERGE new_employees c
FROM employees e ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT INTO
new_employees valueS(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
Answer: A
Q: 14)
Which view should a user query to display the columns associated with the constraints on a table
owned by the user?
A. USER_CONSTRAINTS
B. USER_OBJECTS
C. ALL_CONSTRAINTS
D. USER_CONS_COLUMNS
E. USER_COLUMNS
Answer: D
Q: 15)
The COMMISSION column shows the monthly commission earned by the employee.
Exhibit
Which two tasks would require sub queries or joins in order to be performed in a single step?
(Choose two.)
A. listing the employees who earn the same amount of commission as employee 3
B. finding the total commission earned by the employees in department 10
C. finding the number of employees who earn a commission that is higher than the average
commission of the company
D. listing the departments whose average commission is more that 600
E. listing the employees who do not earn commission and who are working for department 20 in
descending order of the employee ID
F. listing the employees whose annual commission is more than 6000
Answer: A,C
Q:16)
Examine the structure of the STUDENTS table:

You need to create a report of the 10 students who achieved the highest ranking in the course INT
SQL and who completed the course in the year 1999.
Which SQL statement accomplishes this task?
A. SELECT student_ id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank"
FROM students
WHERE ROWNUM <= 10
AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99
AND course_id = 'INT_SQL'
ORDER BY marks DESC;
B. SELECT student_id, marks, ROWID "Rank"
FROM students
WHERE ROWID <= 10
AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99'
AND course_id = 'INT_SQL'
ORDER BY marks;
C. SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank"
FROM (SELECT student_id, marks
FROM students
WHERE ROWNUM <= 10
AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-
99'
AND course_id = 'INT_SQL'
ORDER BY marks DESC);
D. SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank”
FROM (SELECT student_id, marks
FROM students
WHERE (finish_date BETWEEN ’01-JAN-99 AND ’31-DEC-99’
AND course_id = ‘INT_SQL’
ORDER BY marks DESC)
WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 ;
E. SELECTstudent id, marks, ROWNUM “Rank”
FROM(SELECT student_id, marks
FROM students
ORDER BY marks)
WHEREROWNUM <= 10
ANDfinish date BETWEEN ’01-JAN-99’ AND ’31-DEC-99’
ANDcourse_id = ‘INT_SQL’;
Answer: D
QUESTION NO: 17
Evaluate the following SQL statements:
Exhibit:


The above command fails when executed. What could be the reason?
A. The BETWEEN clause cannot be used for the CHECK constraint
B. SYSDATE cannot be used with the CHECK constraint
C. ORD_NO and ITEM_NO cannot be used as a composite primary key because ORD_NO is also
the FOREIGN KEY
D. The CHECK constraint cannot be placed on columns having the DATE data type
Answer: B
Q: 18)
Evaluate the following SQL statements:
DELETE FROM sales;
There are no other uncommitted transactions on the SALES table.
Which statement is true about the DELETE statement?
A. It removes all the rows as well as the structure of the table
B. It removes all the rows in the table and deleted rows cannot be rolled back
C. It removes all the rows in the table and deleted rows can be rolled back
D. It would not remove the rows if the table has a primary key
Answer: C
Q: 19)
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES table:

You want to create a SQL script file that contains an INSERT statement. When the script is run,
the INSERT statement should insert a row with the specified values into the EMPLOYEES table.
The INSERT statement should pass values to the table columns as specified below:

Which INSERT statement meets the above requirements?
A. INSERT INTO employees
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
B. INSERT INTO employees
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid',
2000, NULL, &did IN (20,50));
C. INSERT INTO (SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (20,50))
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
D. INSERT INTO (SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (20,50)
WITH CHECK OPTION)
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
E. INSERT INTO (SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE (department_id = 20 AND
department_id = 50)
WITH CHECK OPTION )
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
Answer: D
Q: 20)
Which two statements are true regarding constraints? (Choose two.)
A. A constraint can be disabled even if the constraint column contains data
B. A constraint is enforced only for the INSERT operation on a table
C. A foreign key cannot contain NULL values
D. All constraints can be defined at the column level as well as the table level
E. A columns with the UNIQUE constraint can contain NULL values
Answer: A,E
Q:21)
Which two statements are true about sequences created in a single instance database? (Choose
two.)
A. CURRVAL is used to refer to the last sequence number that has been generated
B. DELETE <sequencename> would remove a sequence from the database
C. The numbers generated by a sequence can be used only for one table
D. When the MAXVALUE limit for a sequence is reached, you can increase the MAXVALUE limit
by using the ALTER SEQUENCE statement
E. When a database instance shuts down abnormally, the sequence numbers that have been
cached but not used would be available once again when the database instance is restarted
Answer: A,D
Q: 22)
The ORDERS TABLE belongs to the user OE. OE has granted the SELECT privilege on the
ORDERS table to the user HR.
Which statement would create a synonym ORD so that HR can execute the following query
successfully?
SELECT * FROM ord;
A. CREATE SYNONYM ord FOR orders; This command is issued by OE.
B. CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM ord FOR orders; This command is issued by OE.
C. CREATE SYNONYM ord FOR oe.orders; This command is issued by the database
administrator.
D. CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM ord FOR oe.orders; This command is issued by the database
administrator.
Answer: D
Q: 23)
Evaluate this SQL statement:
SELECT e.emp_name, d.dept_name
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d
USING (department_id)
WHERE d.department_id NOT IN (10,40)
ORDER BY dept_name;
The statement fails when executed. Which change fixes the error?
A. remove the ORDER BY clause
B. remove the table alias prefix from the WHERE clause
C. remove the table alias from the SELECT clause
D. prefix the column in the USING clause with the table alias
E. prefix the column in the ORDER BY clause with the table alias
F. replace the condition
”d.department_id NOT IN (10,40)”
in the WHERE clause with
”d.department_id <> 10 AND d.department_id <> 40”
Answer: C,E
Explanation:
Prefix the column in the ORDER BY Clause would cause the statement to succeed, assuming that the statement failed because the dept_name existed in employee & department tables.
Not C: Removing the alias from the columns in the SELECT clause would cause the Statement to fail if the columns existing in both tables.
Q: 24)
Examine the statement:
Create synonym emp for hr.employees;
What happens when you issue the statement?
A. An error is generated.
B. You will have two identical tables in the HR schema with different names.
C. You create a table called employees in the HR schema based on you EMP table.
D. You create an alternative name for the employees table in the HR schema in your own schema.
Answer: D
Q:25)
select trunc( round(156.00,-1),-1) from dual
What would be the outcome?
A. 200
B. 16
C. 160
D. 150
E. 100
Answer:C
Q: 26)
Which two statements are true regarding single row functions? (Choose two.)
A. They can be nested only to two levels
B. They always return a single result row for every row of a queried table
C. Arguments can only be column values or constant
D. They can return a data type value different from the one that is referenced
E. They accept only a single argument
Answer: B,D
Q: 27)
Which statement is true regarding the UNION operator?
A. The number of columns selected in all SELECT statements need to be the same
B. Names of all columns must be identical across all SELECT statements
C. By default, the output is not sorted
D. NULL values are not ignored during duplicate checking
Answer: A
Q: 28)
Which two statements are true regarding working with dates? (Choose two.)
A. The default internal storage of dates is in the numeric format
B. The RR date format automatically calculates the century from the SYSDATE function but allows
the user to enter the century if required
C. The default internal storage of dates is in the character format
D. The RR date format automatically calculates the century from the SYSDATE function and does
not allow the user to enter the century
Answer: A,B
Q:29)
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS table.
INSERT INTO NEW_CUSTOMER(cust_id,cust_name,cust_city)
values(select cust_id,cust_first_name||','||cust_last_name
from customers
where cust_id >23004)
The INSERT statement fails when executed. What could be the reason?
A. The VALUES clause cannot be used in an INSERT with a subquery
B. The total number of columns in the NEW_CUSTOMERS table does not match the total number
of columns in the CUSTOMERS table
C. The WHERE clause cannot be used in a sub query embedded in an INSERT statement
D. Column names in the NEW_CUSTOMERS and CUSTOMERS tables do not match
Answer: A
Q:30)
You want to update the CUST_CREDIT_LIMIT column to NULL for all the customers, where
CUST_INCOME_LEVEL has NULL in the CUSTOMERS table. Which SQL statement will
accomplish the task?
A.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = NULL
WHERE CUST_INCOME_LEVEL = NULL;
B.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = NULL
WHERE cust_income_level IS NULL;
C.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = TO_NUMBER(NULL)
WHERE cust_income_level = TO_NUMBER(NULL);
D.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = TO_NUMBER(' ',9999)
WHERE cust_income_level IS NULL;
Answer: B
Q: 31)
Which two statements about sub queries are true? (Choose two.)
A. A sub query should retrieve only one row.
B. A sub query can retrieve zero or more rows.
C. A sub query can be used only in SQL query statements.
D. Sub queries CANNOT be nested by more than two levels.
E. A sub query CANNOT be used in an SQL query statement that uses group functions.
F. When a sub query is used with an inequality comparison operator in the outer SQL statement,
the column list in the SELECT clause of the sub query should contain only one column.
Answer: B,F
Q:32)
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PROMOTIONS table.
You have to generate a report that displays the promo name and start date for all promos that
started after the last promo in the 'INTERNET' category.
Which query would give you the required output?
A.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date > ALL (SELECT MAX(promo_begin_date) FROM promotions )AND
promo_category = 'INTERNET';
B.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date IN (SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_category='INTERNET');
C.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date > ALL (SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_category = 'INTERNET');
D.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date > ANY (SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_category = 'INTERNET');
Answer: C
Q:33)
SQL*Plus commands? (Choose all that apply.)
A. INSERT
B. UPDATE
C. SELECT
D. DESCRIBE
E. DELETE
F. RENAME
Answer: D
Explanation:
Describe is a valid iSQL*Plus/ SQL*Plus command.
INSERT, UPDATE & DELETE are SQL DML Statements. A SELECT is an ANSI Standard SQL
Statement not an iSQL*Plus Statement.RENAME is a DDL Statement.
Q: 34)
Which two statements are true regarding the COUNT function? (Choose two.)
A. COUNT(*) returns the number of rows including duplicate rows and rows containing NULL
value in any of the columns
B. COUNT(cust_id) returns the number of rows including rows with duplicate customer IDs and
NULL value in the CUST_ID column
C. COUNT(DISTINCT inv_amt) returns the number of rows excluding rows containing duplicates
and NULL values in the INV_AMT column
D. A SELECT statement using COUNT function with a DISTINCT keyword cannot have a WHERE
clause
E. The COUNT function can be used only for CHAR, VARCHAR2 and NUMBER data types
Answer: A,C
Q: 35)
Examine the description of the EMP_DETAILS table given below:
Exhibit:
Name NULL DATATYPE
------------------------------------------------------------
EMP_ID NOTNULL NUMBER
EMP_NAME NOTNULL VARCHAR2(40)
EMP_IMAGE LONG
Which two statements are true regarding SQL statements that can be executed on the
EMP_DETAIL table? (Choose two.)
A. An EMP_IMAGE column can be included in the GROUP BY clause
B. You cannot add a new column to the table with LONG as the data type
C. An EMP_IMAGE column cannot be included in the ORDER BY clause
D. You can alter the table to include the NOT NULL constraint on the EMP_IMAGE column
Answer: B,C
Q:36)
Which CREATE TABLE statement is valid?
A.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2) PRIMARY KEY,
item_no NUMBER(3) PRIMARY KEY,
ord_date DATE NOT NULL);
B.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2) UNIQUE, NOT NULL,
item_no NUMBER(3),
ord_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE NOT NULL);
C.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2) ,
item_no NUMBER(3),
ord_date DATE DEFAULT NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT ord_uq UNIQUE (ord_no),
CONSTRAINT ord_pk PRIMARY KEY (ord_no));
D.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2),
item_no NUMBER(3),
ord_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT ord_pk PRIMARY KEY (ord_no, item_no));
Answer: D
Q:37)
See the exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS and GRADES tables:
CUSTOMER
CUSTNO NOT NULL NUMBER(2)
CUSTNAME VARCHAR2(20)
CUSTADDRESS VARCHAR2(20)
CUST_CREDIT_LIMIT NUMBER(5)
GRADE
GRADEID NOT NULL VARCHAR2(1)
STARTVAL NUMBER(5)
ENDVAL NUMBER(5)
You need to display names and grades of customers who have the highest credit limit.
Which two SQL statements would accomplish the task? (Choose two.)
A.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers, grades
WHERE (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers) BETWEEN startval and endval;
B.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers, grades
WHERE (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers) BETWEEN startval and endval
AND cust_credit_limit BETWEEN startval AND endval;
C.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers, grades
WHERE cust_credit_limit = (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers)
AND cust_credit_limit BETWEEN startval AND endval;
D.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers , grades
WHERE cust_credit_limit IN (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers)
AND MAX(cust_credit_limit) BETWEEN startval AND endval;
Answer: B,C
Q:38)See the Exhibit and Examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS table
Using the CUSTOMERS table, you need to generate a report that shows an increase in the credit
limit by 15% for all customers. Customers whose credit limit has not been entered should have the
message "Not Available" displayed.
Which SQL statement would produce the required result?
A. SELECT NVL(cust_credit_limit,'Not Available')*.15 "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
B. SELECT NVL(cust_credit_limit*.15,'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
C. SELECT TO_CHAR(NVL(cust_credit_limit*.15,'Not Available')) "NEW CREDIT" FROM
customers;
D. SELECT NVL(TO_CHAR(cust_credit_limit*.15),'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM
customers;
Answer: D
Q: 39)
You need to calculate the number of days from 1st Jan 2007 till date:
Dates are stored in the default format of dd-mm-rr.
Which two SQL statements would give the required output? (Choose two.)
A. SELECT SYSDATE - TO_DATE('01/JANUARY/2007') FROM DUAL;
B. SELECT TO_DATE(SYSDATE,'DD/MONTH/YYYY')-'01/JANUARY/2007' FROM DUAL;
C. SELECT SYSDATE - TO_DATE('01-JANUARY-2007') FROM DUAL
D. SELECT SYSDATE - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL
E. SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'DD-MON-YYYY')-'01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL;
Answer: A,C
Q:40)
Which two are true about aggregate functions? (Choose two.)
A. You can use aggregate functions in any clause of a SELECT statement.
B. You can use aggregate functions only in the column list of the select clause and in the WHERE
clause of a SELECT statement.
C. You can mix single row columns with aggregate functions in the column list of a SELECT
statement by grouping on the single row columns.
D. You can pass column names, expressions, constants, or functions as parameter to an
aggregate function.
E. You can use aggregate functions on a table, only by grouping the whole table as one single
group.
F. You cannot group the rows of a table by more than one column while using aggregate
functions.
Answer: A,D
Q:41)
See the structure of the PROGRAMS table:
NAME NULL TYPE
-------------------------------------------------
PROG_ID NOTNULL NUMBER(3)
PROG_COST NUMBER(8,2)
START_DATE NOT NULL DATE
END-DATE DATE
Which two SQL statements would execute successfully? (Choose two.)
A. SELECT NVL(ADD_MONTHS(END_DATE,1),SYSDATE)
FROM programs;
B. SELECT TO_DATE(NVL(SYSDATE-END_DATE,SYSDATE))
FROM programs;
C. SELECT NVL(MONTHS_BETWEEN(start_date,end_date),'Ongoing')
FROM programs;
D. SELECT NVL(TO_CHAR(MONTHS_BETWEEN(start_date,end_date)),'Ongoing') FROM
programs;
Answer: A,D
Q:42)
You issue the following command to drop the PRODUCTS table:
SQL>DROP TABLE products;
What is the implication of this command? (Choose all that apply.)
A. All data in the table are deleted but the table structure will remain
B. All data along with the table structure is deleted
C. All views and synonyms will remain but they are invalidated
D. The pending transaction in the session is committed
E. All indexes on the table will remain but they are invalidated
Answer: B,C,D
Q:43)
Table PRODUCTS
NAME NULL TYPE
--------------------------------------------------------
PROD_ID NOTNULL NUMBER(6)
PROD_NAME NOTNULL varchar2(50)
PROD_DESC NOTNULL VARCHAR2(50)
PROD_CATEGORY NOTNULL VARCHAR2(4000)
PROD_CATEGORY_ID NOTNULL NUMBER
PROD_UNIT_OF_MEASURE VARCHAR2(50)
SUPPLIER_ID NOTNULL NUMBER(6)
PROD_STATUS NOTNULL VARCHAR2(20)
PROD_LIST_PRICE NOTNULL NUMBER(8,2)
PROD_MIN_PRICE NOTNULL NUMBER(8,2)
Evaluate the SQL statement:
TRUNCATE TABLE DEPT;
Which three are true about the SQL statement? (Choose three.)
A. It releases the storage space used by the table.
B. It does not release the storage space used by the table.
C. You can roll back the deletion of rows after the statement executes.
D. You can NOT roll back the deletion of rows after the statement executes.
E. An attempt to use DESCRIBE on the DEPT table after the TRUNCATE statement executes will
display an error.
F. You must be the owner of the table or have DELETE ANY TABLE system privileges to truncate
the DEPT table
Answer:A,D,F
Q:2)
QUESTION NO: 2
You need to design a student registration database that contains several tables storing academic
information.
The STUDENTS table stores information about a student. The STUDENT_GRADES table stores information about the student's grades. Both of the tables have a column named STUDENT_ID.
The STUDENT_ID column in the STUDENTS table is a primary key.
You need to create a foreign key on the STUDENT_ID column of the STUDENT_GRADES table
that points to the STUDENT_ID column of the STUDENTS table. Which statement creates the
foreign key?
A. CREATE TABLE student_grades (student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), CONSTRAINT student_id_fk REFERENCES (student_id) FOREIGN KEY
students(student_id));
B. CREATE TABLE student_grades(student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), student_id_fk FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(student_id));
C. CREATE TABLE student_grades(student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES students(student_id));
D. CREATE TABLE student_grades(student_id NUMBER(12),semester_end DATE, gpa
NUMBER(4,3), CONSTRAINT student_id_fk FOREIGN KEY (student_id) REFERENCES
students(student_id));
Answer: D
Q:3)
Here is the structure and data of the CUST_TRANS table:
Dates are stored in the default date format dd-mm-rr in the CUST_TRANS table.
Which three SQL statements would execute successfully? (Choose three.)
A. SELECT transdate + '10' FROM cust_trans;
B. SELECT * FROM cust_trans WHERE transdate = '01-01-07';
C. SELECT transamt FROM cust_trans WHERE custno > '11';
D. SELECT * FROM cust_trans WHERE transdate='01-JANUARY-07';
E. SELECT custno + 'A' FROM cust_trans WHERE transamt > 2000;
Answer: A,C,D
Q:4)
See the Exhibit and examine the structure and data in the INVOICE table:
Which two SQL statements would executes successfully? (Choose two.)
A. SELECT MAX(inv_date),MIN(cust_id) FROM invoice;
B. SELECT MAX(AVG(SYSDATE - inv_date)) FROM invoice;
C. SELECT (AVG(inv_date) FROM invoice;
D. SELECT AVG(inv_date - SYSDATE),AVG(inv_amt) FROM invoice;
Answer: A,D
Q:5)
QUESTION NO: 5
Which three statements are true regarding sub queries? (Choose three.)
A. Multiple columns or expressions can be compared between the main query and sub query
B. Main query and sub query can get data from different tables
C. Sub queries can contain GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses
D. Main query and sub query must get data from the same tables
E. Sub queries can contain ORDER BY but not the GROUP BY clause
F. Only one column or expression can be compared between the main query and subqeury
Answer: A,B,C
Q:6)See the Exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS table:
Using the CUSTOMERS table, you need to generate a report that shown the average credit limit
for customers in WASHINGTON and NEW YORK.
Which SQL statement would produce the required result?
A.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK')
GROUP BY cust_credit_limit, cust_city;
B.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK')
GROUP BY cust_city,cust_credit_limit;
C.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK')
GROUP BY cust_city;
D.
SELECT cust_city, AVG(NVL(cust_credit_limit,0))
FROM customers
WHERE cust_city IN ('WASHINGTON','NEW YORK');
Answer: C
Q:7)
Evaluate these two SQL statements:
SELECT last_name, salary, hire_date FROM EMPLOYEES ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT last_name, salary, hire_date FROM EMPLOYEES ORDER BY 2 DESC;
What is true about them?
A. The two statements produce identical results.
B. The second statement returns a syntax error.
C. There is no need to specify DESC because the results are sorted in descending order by
default.
D. The two statements can be made to produce identical results by adding a column alias for the
salary column in the second SQL statement.
Answer: A
Q:8)
Where can sub queries be used? (Choose all that apply)
A. field names in the SELECT statement
B. the FROM clause in the SELECT statement
C. the HAVING clause in the SELECT statement
D. the GROUP BY clause in the SELECT statement
E. the WHERE clause in only the SELECT statement
F. the WHERE clause in SELECT as well as all DML statements
Answer: A,B,C,F
Q:9)
Which three SQL statements would display the value 1890.55 as $1,890.55? (Choose three.)
A.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$99G999D00')
FROM DUAL;
B.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$9,999V99')
FROM DUAL;
C.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$0G000D00')
FROM DUAL;
D.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$99G999D99')
FROM DUAL;
E.
SELECT TO_CHAR(1890.55,'$9,999D99')
FROM DUAL;
Answer: A,C,D
Q:10)
Evaluate the following SQL statement:
A. It produces an error because the ORDER BY clause should appear only at the end of a
compound query-that is, with the last SELECT statement
B. It executes successfully and displays rows in the descending order of PROMO_CATEGORY
C. It executes successfully but ignores the ORDER BY clause because it is not located at the end
of the compound statement
D. It produces an error because positional notation cannot be used in the ORDER BY clause with
SET operators
Answer: A
Q: 11)
Which statement correctly describes SQL and /SQL*Plus?
A. Both SQL and /SQL*plus allow manipulation of values in the database.
B. /SQL*Plus recognizes SQL statements and sends them to the server; SQL is the Oracle
proprietary interface for executing SQL statements.
C. /SQL*Plus is a language for communicating with the Oracle server to access data; SQL
recognizes SQL statements and sends them to the server.
D. SQL manipulates data and table definitions in the database; /SQL*Plus does not allow
manipulation of values in the database.
Answer: A
Q: 12)
Which four are types of functions available in SQL? (Choose 4)
A. string
B. character
C. integer
D. calendar
E. numeric
F. translation
G. date
H. conversion
Answer: B,E,G,H
Q:13)
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES and NEW_EMPLOYEES tables:
A.
MERGE INTO new_employees c
USING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT
value
S(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
B.
MERGE new_employees c
USING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN EXISTS THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT
valueS(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
Oracle 1z0-051 Exam
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 11
C.
MERGE INTO new_employees cUSING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN EXISTS THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT
value
S(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
D.MERGE new_employees c
FROM employees e ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE
MERGE INTO new_employees cUSING employees e
ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN EXISTS THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT
value
S(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
E.MERGE new_employees c
FROM employees e ON (c.employee_id = e.employee_id)
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
name = e.first_name ||','|| e.last_name
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT INTO
new_employees valueS(e.employee_id, e.first_name ||',
'||e.last_name);
Answer: A
Q: 14)
Which view should a user query to display the columns associated with the constraints on a table
owned by the user?
A. USER_CONSTRAINTS
B. USER_OBJECTS
C. ALL_CONSTRAINTS
D. USER_CONS_COLUMNS
E. USER_COLUMNS
Answer: D
Q: 15)
The COMMISSION column shows the monthly commission earned by the employee.
Exhibit
Which two tasks would require sub queries or joins in order to be performed in a single step?
(Choose two.)
A. listing the employees who earn the same amount of commission as employee 3
B. finding the total commission earned by the employees in department 10
C. finding the number of employees who earn a commission that is higher than the average
commission of the company
D. listing the departments whose average commission is more that 600
E. listing the employees who do not earn commission and who are working for department 20 in
descending order of the employee ID
F. listing the employees whose annual commission is more than 6000
Answer: A,C
Q:16)
Examine the structure of the STUDENTS table:

SQL and who completed the course in the year 1999.
Which SQL statement accomplishes this task?
A. SELECT student_ id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank"
FROM students
WHERE ROWNUM <= 10
AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99
AND course_id = 'INT_SQL'
ORDER BY marks DESC;
B. SELECT student_id, marks, ROWID "Rank"
FROM students
WHERE ROWID <= 10
AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-99'
AND course_id = 'INT_SQL'
ORDER BY marks;
C. SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank"
FROM (SELECT student_id, marks
FROM students
WHERE ROWNUM <= 10
AND finish_date BETWEEN '01-JAN-99' AND '31-DEC-
99'
AND course_id = 'INT_SQL'
ORDER BY marks DESC);
D. SELECT student_id, marks, ROWNUM "Rank”
FROM (SELECT student_id, marks
FROM students
WHERE (finish_date BETWEEN ’01-JAN-99 AND ’31-DEC-99’
AND course_id = ‘INT_SQL’
ORDER BY marks DESC)
WHERE ROWNUM <= 10 ;
E. SELECTstudent id, marks, ROWNUM “Rank”
FROM(SELECT student_id, marks
FROM students
ORDER BY marks)
WHEREROWNUM <= 10
ANDfinish date BETWEEN ’01-JAN-99’ AND ’31-DEC-99’
ANDcourse_id = ‘INT_SQL’;
Answer: D
QUESTION NO: 17
Evaluate the following SQL statements:
Exhibit:


The above command fails when executed. What could be the reason?
A. The BETWEEN clause cannot be used for the CHECK constraint
B. SYSDATE cannot be used with the CHECK constraint
C. ORD_NO and ITEM_NO cannot be used as a composite primary key because ORD_NO is also
the FOREIGN KEY
D. The CHECK constraint cannot be placed on columns having the DATE data type
Answer: B
Q: 18)
Evaluate the following SQL statements:
DELETE FROM sales;
There are no other uncommitted transactions on the SALES table.
Which statement is true about the DELETE statement?
A. It removes all the rows as well as the structure of the table
B. It removes all the rows in the table and deleted rows cannot be rolled back
C. It removes all the rows in the table and deleted rows can be rolled back
D. It would not remove the rows if the table has a primary key
Answer: C
Q: 19)
Examine the structure of the EMPLOYEES table:

You want to create a SQL script file that contains an INSERT statement. When the script is run,
the INSERT statement should insert a row with the specified values into the EMPLOYEES table.
The INSERT statement should pass values to the table columns as specified below:

Which INSERT statement meets the above requirements?
A. INSERT INTO employees
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
B. INSERT INTO employees
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid',
2000, NULL, &did IN (20,50));
C. INSERT INTO (SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (20,50))
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
D. INSERT INTO (SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (20,50)
WITH CHECK OPTION)
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
E. INSERT INTO (SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE (department_id = 20 AND
department_id = 50)
WITH CHECK OPTION )
VALUES (emp_id_seq.NEXTVAL, '&ename', '&jobid', 2000, NULL, &did);
Answer: D
Q: 20)
Which two statements are true regarding constraints? (Choose two.)
A. A constraint can be disabled even if the constraint column contains data
B. A constraint is enforced only for the INSERT operation on a table
C. A foreign key cannot contain NULL values
D. All constraints can be defined at the column level as well as the table level
E. A columns with the UNIQUE constraint can contain NULL values
Answer: A,E
Q:21)
Which two statements are true about sequences created in a single instance database? (Choose
two.)
A. CURRVAL is used to refer to the last sequence number that has been generated
B. DELETE <sequencename> would remove a sequence from the database
C. The numbers generated by a sequence can be used only for one table
D. When the MAXVALUE limit for a sequence is reached, you can increase the MAXVALUE limit
by using the ALTER SEQUENCE statement
E. When a database instance shuts down abnormally, the sequence numbers that have been
cached but not used would be available once again when the database instance is restarted
Answer: A,D
Q: 22)
The ORDERS TABLE belongs to the user OE. OE has granted the SELECT privilege on the
ORDERS table to the user HR.
Which statement would create a synonym ORD so that HR can execute the following query
successfully?
SELECT * FROM ord;
A. CREATE SYNONYM ord FOR orders; This command is issued by OE.
B. CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM ord FOR orders; This command is issued by OE.
C. CREATE SYNONYM ord FOR oe.orders; This command is issued by the database
administrator.
D. CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM ord FOR oe.orders; This command is issued by the database
administrator.
Answer: D
Q: 23)
Evaluate this SQL statement:
SELECT e.emp_name, d.dept_name
FROM employees e
JOIN departments d
USING (department_id)
WHERE d.department_id NOT IN (10,40)
ORDER BY dept_name;
The statement fails when executed. Which change fixes the error?
A. remove the ORDER BY clause
B. remove the table alias prefix from the WHERE clause
C. remove the table alias from the SELECT clause
D. prefix the column in the USING clause with the table alias
E. prefix the column in the ORDER BY clause with the table alias
F. replace the condition
”d.department_id NOT IN (10,40)”
in the WHERE clause with
”d.department_id <> 10 AND d.department_id <> 40”
Answer: C,E
Explanation:
Prefix the column in the ORDER BY Clause would cause the statement to succeed, assuming that the statement failed because the dept_name existed in employee & department tables.
Not C: Removing the alias from the columns in the SELECT clause would cause the Statement to fail if the columns existing in both tables.
Q: 24)
Examine the statement:
Create synonym emp for hr.employees;
What happens when you issue the statement?
A. An error is generated.
B. You will have two identical tables in the HR schema with different names.
C. You create a table called employees in the HR schema based on you EMP table.
D. You create an alternative name for the employees table in the HR schema in your own schema.
Answer: D
Q:25)
select trunc( round(156.00,-1),-1) from dual
What would be the outcome?
A. 200
B. 16
C. 160
D. 150
E. 100
Answer:C
Q: 26)
Which two statements are true regarding single row functions? (Choose two.)
A. They can be nested only to two levels
B. They always return a single result row for every row of a queried table
C. Arguments can only be column values or constant
D. They can return a data type value different from the one that is referenced
E. They accept only a single argument
Answer: B,D
Q: 27)
Which statement is true regarding the UNION operator?
A. The number of columns selected in all SELECT statements need to be the same
B. Names of all columns must be identical across all SELECT statements
C. By default, the output is not sorted
D. NULL values are not ignored during duplicate checking
Answer: A
Q: 28)
Which two statements are true regarding working with dates? (Choose two.)
A. The default internal storage of dates is in the numeric format
B. The RR date format automatically calculates the century from the SYSDATE function but allows
the user to enter the century if required
C. The default internal storage of dates is in the character format
D. The RR date format automatically calculates the century from the SYSDATE function and does
not allow the user to enter the century
Answer: A,B
Q:29)
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS table.
INSERT INTO NEW_CUSTOMER(cust_id,cust_name,cust_city)
values(select cust_id,cust_first_name||','||cust_last_name
from customers
where cust_id >23004)
The INSERT statement fails when executed. What could be the reason?
A. The VALUES clause cannot be used in an INSERT with a subquery
B. The total number of columns in the NEW_CUSTOMERS table does not match the total number
of columns in the CUSTOMERS table
C. The WHERE clause cannot be used in a sub query embedded in an INSERT statement
D. Column names in the NEW_CUSTOMERS and CUSTOMERS tables do not match
Answer: A
Q:30)
You want to update the CUST_CREDIT_LIMIT column to NULL for all the customers, where
CUST_INCOME_LEVEL has NULL in the CUSTOMERS table. Which SQL statement will
accomplish the task?
A.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = NULL
WHERE CUST_INCOME_LEVEL = NULL;
B.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = NULL
WHERE cust_income_level IS NULL;
C.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = TO_NUMBER(NULL)
WHERE cust_income_level = TO_NUMBER(NULL);
D.
UPDATE customers
SET cust_credit_limit = TO_NUMBER(' ',9999)
WHERE cust_income_level IS NULL;
Answer: B
Q: 31)
Which two statements about sub queries are true? (Choose two.)
A. A sub query should retrieve only one row.
B. A sub query can retrieve zero or more rows.
C. A sub query can be used only in SQL query statements.
D. Sub queries CANNOT be nested by more than two levels.
E. A sub query CANNOT be used in an SQL query statement that uses group functions.
F. When a sub query is used with an inequality comparison operator in the outer SQL statement,
the column list in the SELECT clause of the sub query should contain only one column.
Answer: B,F
Q:32)
View the Exhibit and examine the structure of the PROMOTIONS table.
You have to generate a report that displays the promo name and start date for all promos that
started after the last promo in the 'INTERNET' category.
Which query would give you the required output?
A.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date > ALL (SELECT MAX(promo_begin_date) FROM promotions )AND
promo_category = 'INTERNET';
B.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date IN (SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_category='INTERNET');
C.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date > ALL (SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_category = 'INTERNET');
D.
SELECT promo_name, promo_begin_date FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date > ANY (SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_category = 'INTERNET');
Answer: C
Q:33)
SQL*Plus commands? (Choose all that apply.)
A. INSERT
B. UPDATE
C. SELECT
D. DESCRIBE
E. DELETE
F. RENAME
Answer: D
Explanation:
Describe is a valid iSQL*Plus/ SQL*Plus command.
INSERT, UPDATE & DELETE are SQL DML Statements. A SELECT is an ANSI Standard SQL
Statement not an iSQL*Plus Statement.RENAME is a DDL Statement.
Q: 34)
Which two statements are true regarding the COUNT function? (Choose two.)
A. COUNT(*) returns the number of rows including duplicate rows and rows containing NULL
value in any of the columns
B. COUNT(cust_id) returns the number of rows including rows with duplicate customer IDs and
NULL value in the CUST_ID column
C. COUNT(DISTINCT inv_amt) returns the number of rows excluding rows containing duplicates
and NULL values in the INV_AMT column
D. A SELECT statement using COUNT function with a DISTINCT keyword cannot have a WHERE
clause
E. The COUNT function can be used only for CHAR, VARCHAR2 and NUMBER data types
Answer: A,C
Q: 35)
Examine the description of the EMP_DETAILS table given below:
Exhibit:
Name NULL DATATYPE
------------------------------------------------------------
EMP_ID NOTNULL NUMBER
EMP_NAME NOTNULL VARCHAR2(40)
EMP_IMAGE LONG
Which two statements are true regarding SQL statements that can be executed on the
EMP_DETAIL table? (Choose two.)
A. An EMP_IMAGE column can be included in the GROUP BY clause
B. You cannot add a new column to the table with LONG as the data type
C. An EMP_IMAGE column cannot be included in the ORDER BY clause
D. You can alter the table to include the NOT NULL constraint on the EMP_IMAGE column
Answer: B,C
Q:36)
Which CREATE TABLE statement is valid?
A.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2) PRIMARY KEY,
item_no NUMBER(3) PRIMARY KEY,
ord_date DATE NOT NULL);
B.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2) UNIQUE, NOT NULL,
item_no NUMBER(3),
ord_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE NOT NULL);
C.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2) ,
item_no NUMBER(3),
ord_date DATE DEFAULT NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT ord_uq UNIQUE (ord_no),
CONSTRAINT ord_pk PRIMARY KEY (ord_no));
D.
CREATE TABLE ord_details
(ord_no NUMBER(2),
item_no NUMBER(3),
ord_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT ord_pk PRIMARY KEY (ord_no, item_no));
Answer: D
Q:37)
See the exhibit and examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS and GRADES tables:
CUSTOMER
CUSTNO NOT NULL NUMBER(2)
CUSTNAME VARCHAR2(20)
CUSTADDRESS VARCHAR2(20)
CUST_CREDIT_LIMIT NUMBER(5)
GRADE
GRADEID NOT NULL VARCHAR2(1)
STARTVAL NUMBER(5)
ENDVAL NUMBER(5)
You need to display names and grades of customers who have the highest credit limit.
Which two SQL statements would accomplish the task? (Choose two.)
A.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers, grades
WHERE (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers) BETWEEN startval and endval;
B.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers, grades
WHERE (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers) BETWEEN startval and endval
AND cust_credit_limit BETWEEN startval AND endval;
C.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers, grades
WHERE cust_credit_limit = (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers)
AND cust_credit_limit BETWEEN startval AND endval;
D.
SELECT custname, grade
FROM customers , grades
WHERE cust_credit_limit IN (SELECT MAX(cust_credit_limit)
FROM customers)
AND MAX(cust_credit_limit) BETWEEN startval AND endval;
Answer: B,C
Q:38)See the Exhibit and Examine the structure of the CUSTOMERS table
Using the CUSTOMERS table, you need to generate a report that shows an increase in the credit
limit by 15% for all customers. Customers whose credit limit has not been entered should have the
message "Not Available" displayed.
Which SQL statement would produce the required result?
A. SELECT NVL(cust_credit_limit,'Not Available')*.15 "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
B. SELECT NVL(cust_credit_limit*.15,'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM customers;
C. SELECT TO_CHAR(NVL(cust_credit_limit*.15,'Not Available')) "NEW CREDIT" FROM
customers;
D. SELECT NVL(TO_CHAR(cust_credit_limit*.15),'Not Available') "NEW CREDIT" FROM
customers;
Answer: D
Q: 39)
You need to calculate the number of days from 1st Jan 2007 till date:
Dates are stored in the default format of dd-mm-rr.
Which two SQL statements would give the required output? (Choose two.)
A. SELECT SYSDATE - TO_DATE('01/JANUARY/2007') FROM DUAL;
B. SELECT TO_DATE(SYSDATE,'DD/MONTH/YYYY')-'01/JANUARY/2007' FROM DUAL;
C. SELECT SYSDATE - TO_DATE('01-JANUARY-2007') FROM DUAL
D. SELECT SYSDATE - '01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL
E. SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'DD-MON-YYYY')-'01-JAN-2007' FROM DUAL;
Answer: A,C
Q:40)
Which two are true about aggregate functions? (Choose two.)
A. You can use aggregate functions in any clause of a SELECT statement.
B. You can use aggregate functions only in the column list of the select clause and in the WHERE
clause of a SELECT statement.
C. You can mix single row columns with aggregate functions in the column list of a SELECT
statement by grouping on the single row columns.
D. You can pass column names, expressions, constants, or functions as parameter to an
aggregate function.
E. You can use aggregate functions on a table, only by grouping the whole table as one single
group.
F. You cannot group the rows of a table by more than one column while using aggregate
functions.
Answer: A,D
Q:41)
See the structure of the PROGRAMS table:
NAME NULL TYPE
-------------------------------------------------
PROG_ID NOTNULL NUMBER(3)
PROG_COST NUMBER(8,2)
START_DATE NOT NULL DATE
END-DATE DATE
Which two SQL statements would execute successfully? (Choose two.)
A. SELECT NVL(ADD_MONTHS(END_DATE,1),SYSDATE)
FROM programs;
B. SELECT TO_DATE(NVL(SYSDATE-END_DATE,SYSDATE))
FROM programs;
C. SELECT NVL(MONTHS_BETWEEN(start_date,end_date),'Ongoing')
FROM programs;
D. SELECT NVL(TO_CHAR(MONTHS_BETWEEN(start_date,end_date)),'Ongoing') FROM
programs;
Answer: A,D
Q:42)
You issue the following command to drop the PRODUCTS table:
SQL>DROP TABLE products;
What is the implication of this command? (Choose all that apply.)
A. All data in the table are deleted but the table structure will remain
B. All data along with the table structure is deleted
C. All views and synonyms will remain but they are invalidated
D. The pending transaction in the session is committed
E. All indexes on the table will remain but they are invalidated
Answer: B,C,D
Q:43)
Table PRODUCTS
NAME NULL TYPE
--------------------------------------------------------
PROD_ID NOTNULL NUMBER(6)
PROD_NAME NOTNULL varchar2(50)
PROD_DESC NOTNULL VARCHAR2(50)
PROD_CATEGORY NOTNULL VARCHAR2(4000)
PROD_CATEGORY_ID NOTNULL NUMBER
PROD_UNIT_OF_MEASURE VARCHAR2(50)
SUPPLIER_ID NOTNULL NUMBER(6)
PROD_STATUS NOTNULL VARCHAR2(20)
PROD_LIST_PRICE NOTNULL NUMBER(8,2)
PROD_MIN_PRICE NOTNULL NUMBER(8,2)
SELECT PROD_NAME
FROM PRODUCTS
WHERE PROD_ID IN(SELECT PROD_ID FROM
PRODUCTS
WHERE PROD_LIST_PRICE =(SELECT MAX(PRODUCT_LIST_PRICE)
FROM PRODUCTS
WHERE PRODUCT_LIST_PRICE<
(SELECT MAX(PRODUCT_LIST_PRICE)
FROM PRODUCTS)))
What would be the outcome of executing the above SQL statement?
A. It produces an error
B. It shows the names of products whose list price is the second highest in the table.
C. It shown the names of all products whose list price is less than the maximum list price
D. It shows the names of all products in the table
Answer: B
Explanation:
Q:44)
select p.product_id,prod_name,prod_list_price,
quantity_sold,cust_last_name
from products p natural join sales s natural join customers c
where prod_id =148
Which statement is true regarding the outcome of this query?
A. It produces an error because the NATURAL join can be used only with two tables
B. It produces an error because a column used in the NATURAL join cannot have a qualifier
C. It produces an error because all columns used in the NATURAL join should have a qualifier
D. It executes successfully
Answer: B
Q:45)
create view sales_product
select p.product_id,cust_id,sum(quantity_sol)"quantity",sum(prod_list_price)
from products p sales s
where p.prod_id =s.prod_id
Which statement is true regarding the execution of the above statement?
A. The view will be created and you can perform DLM operations on the view
B. The view will not be created because the join statements are not allowed for creating a view
C. The view will not be created because the GROUP BY clause is not allowed for creating a view
D. The view will be created but no DML operations will be allowed on the view
Answer: D
Q: 46)
Which three statements are true regarding the data types in Oracle Database 10g/11g? (Choose
three.)
A. The BLOB data type column is used to store binary data in an operating system file
B. The minimum column width that can be specified for a VARCHAR2 data type column is one
C. A TIMESTAMP data type column stores only time values with fractional seconds
D. The value for a CHAR data type column is blank-padded to the maximum defined column width
E. Only One LONG column can be used per table
Answer: B,D,E
Q: 47)
Which three are true? (Choose three.)
A. A MERGE statement is used to merge the data of one table with data from another.
Oracle 1z0-051 Exam
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 39
B. A MERGE statement replaces the data of one table with that of another.
C. A MERGE statement can be used to insert new rows into a table.
D. A MERGE statement can be used to update existing rows in a table.
Answer: A,C,D
Q: 48)
Which two statements are true regarding views? (Choose two.)
A. A sub query that defines a view cannot include the GROUP BY clause
B. A view is created with the sub query having the DISTINCT keyword can be updated
C. A Data Manipulation Language (DML) operation can be performed on a view that is created
with the sub query having all the NOT NULL columns of a table
D. A view that is created with the sub query having the pseudo column ROWNUM keyword cannot
be updated
Answer: C,D
Q:49)
Which DELETE statement is valid?
A. DELETE FROM employeesWHERE employee_id = (SELECT employee_id FROM employees);
B. DELETE * FROM employeesWHERE employee_id=(SELECT employee_id FROM
new_employees);
C. DELETE FROM employeesWHERE employee_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM
new_employees WHERE name = ‘Carrey’);
D. DELETE * FROM employeesWHERE employee_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM
new_employees WHERE name = ‘Carrey’);
Answer: C
Q:50)
SQL)select p.prom_id,p.promo_name,s.prod_id
from sales s right outer join promotions p
on(s.promo_id=p.promo_id);
Which statement is true regarding the output of the above query?
A. It gives details of product IDs that have been sold irrespective of whether they had a promo or
not
B. It gives the details of promos for which there have been no sales
C. It gives the details of promos for which there have been sales
D. It gives details of all promos irrespective of whether they have resulted in a sale or not
Answer: D
Q:51)
Employees
Employee_id number primary key
first_name varchar2(25)
last_name varchar2(25)
hire_date date
Which UPDATE statement is valid?
A.
UPDATE employees
SET first_name = ‘John’
SET last_name = ‘Smith’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
B.
UPDATE employees
SET first_name = ‘John’,
SET last_name = ‘Smoth’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
C.
UPDATE employee
SET first_name = ‘John’
AND last_name = ‘Smith’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
D.
UPDATE employee
SET first_name = ‘John’, last_name = ‘Smith’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
Answer: D
Q:52)
select prod_id from products
intersect
selcet prod_id from sales
minus
select prod_id from costs;
Which statement is true regarding the above compound query?
A. It shows products that have a cost recorded irrespective of sales
B. It shows products that were sold and have a cost recorded
C. It shows products that were sold but have no cost recorded
D. It reduces an error
Answer: C
Q:53)
The products table has following structure:
Name NULL DATATYPE
------------------------------------
prod_id Notnull number(4)
prod_name varchar2(25)
prod_expiry_date date
SQL>SELECT PROD_ID,NVL2(PROD_EXPIRY_DATE,PROD_EXPIRY_DATE + 15,'') FROM PRODUCTS;
SQL>SELECT PROD_ID,NVL(PROD_EXPIRY_DATE,PROD_EXPIRY_DATE_15) FROM PRODUCTS;
Which statement is true regarding the outcome?
A. Both the statements execute and give the same result
B. Both the statements execute and give different results
C. Only the second SQL statement executes successfully
D. Only the first SQL statement executes successfully
Answer: B
Q: 54)
Which statements are correct regarding indexes? (Choose all that apply.)
A. For each data manipulation language (DML) operation performed, the corresponding indexes
are automatically updated.
B. A nondeferrable PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE KEY constraint in a table automatically creates a
unique index.
C. A FOREIGN KEY constraint on a column in a table automatically creates a non unique key
D. When a table is dropped, the corresponding indexes are automatically dropped
Answer: A,B,D
Q:55)
Which two SQL statements would execute successfully? (Choose two.)
A.
UPDATE promotions
SET promo_cost = promo_cost+ 100
WHERE TO_CHAR(promo_end_date, 'yyyy') > '2000';
B.
SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE TO_CHAR(promo_begin_date,'mon dd yy')='jul 01 98';
C.
UPDATE promotions
SET promo_cost = promo_cost+ 100
WHERE promo_end_date > TO_DATE(SUBSTR('01-JAN-2000',8));
D.
SELECT TO_CHAR(promo_begin_date,'dd/month')
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date IN (TO_DATE('JUN 01 98'), TO_DATE('JUL 01 98'));
Answer: A,B
quantity_sold,cust_last_name
from products p natural join sales s natural join customers c
where prod_id =148
Which statement is true regarding the outcome of this query?
A. It produces an error because the NATURAL join can be used only with two tables
B. It produces an error because a column used in the NATURAL join cannot have a qualifier
C. It produces an error because all columns used in the NATURAL join should have a qualifier
D. It executes successfully
Answer: B
Q:45)
create view sales_product
select p.product_id,cust_id,sum(quantity_sol)"quantity",sum(prod_list_price)
from products p sales s
where p.prod_id =s.prod_id
Which statement is true regarding the execution of the above statement?
A. The view will be created and you can perform DLM operations on the view
B. The view will not be created because the join statements are not allowed for creating a view
C. The view will not be created because the GROUP BY clause is not allowed for creating a view
D. The view will be created but no DML operations will be allowed on the view
Answer: D
Q: 46)
Which three statements are true regarding the data types in Oracle Database 10g/11g? (Choose
three.)
A. The BLOB data type column is used to store binary data in an operating system file
B. The minimum column width that can be specified for a VARCHAR2 data type column is one
C. A TIMESTAMP data type column stores only time values with fractional seconds
D. The value for a CHAR data type column is blank-padded to the maximum defined column width
E. Only One LONG column can be used per table
Answer: B,D,E
Q: 47)
Which three are true? (Choose three.)
A. A MERGE statement is used to merge the data of one table with data from another.
Oracle 1z0-051 Exam
"Pass Any Exam. Any Time." - www.actualtests.com 39
B. A MERGE statement replaces the data of one table with that of another.
C. A MERGE statement can be used to insert new rows into a table.
D. A MERGE statement can be used to update existing rows in a table.
Answer: A,C,D
Q: 48)
Which two statements are true regarding views? (Choose two.)
A. A sub query that defines a view cannot include the GROUP BY clause
B. A view is created with the sub query having the DISTINCT keyword can be updated
C. A Data Manipulation Language (DML) operation can be performed on a view that is created
with the sub query having all the NOT NULL columns of a table
D. A view that is created with the sub query having the pseudo column ROWNUM keyword cannot
be updated
Answer: C,D
Q:49)
Which DELETE statement is valid?
A. DELETE FROM employeesWHERE employee_id = (SELECT employee_id FROM employees);
B. DELETE * FROM employeesWHERE employee_id=(SELECT employee_id FROM
new_employees);
C. DELETE FROM employeesWHERE employee_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM
new_employees WHERE name = ‘Carrey’);
D. DELETE * FROM employeesWHERE employee_id IN (SELECT employee_id FROM
new_employees WHERE name = ‘Carrey’);
Answer: C
Q:50)
SQL)select p.prom_id,p.promo_name,s.prod_id
from sales s right outer join promotions p
on(s.promo_id=p.promo_id);
Which statement is true regarding the output of the above query?
A. It gives details of product IDs that have been sold irrespective of whether they had a promo or
not
B. It gives the details of promos for which there have been no sales
C. It gives the details of promos for which there have been sales
D. It gives details of all promos irrespective of whether they have resulted in a sale or not
Answer: D
Q:51)
Employees
Employee_id number primary key
first_name varchar2(25)
last_name varchar2(25)
hire_date date
Which UPDATE statement is valid?
A.
UPDATE employees
SET first_name = ‘John’
SET last_name = ‘Smith’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
B.
UPDATE employees
SET first_name = ‘John’,
SET last_name = ‘Smoth’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
C.
UPDATE employee
SET first_name = ‘John’
AND last_name = ‘Smith’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
D.
UPDATE employee
SET first_name = ‘John’, last_name = ‘Smith’
WHERE employee_id = 180;
Answer: D
Q:52)
select prod_id from products
intersect
selcet prod_id from sales
minus
select prod_id from costs;
Which statement is true regarding the above compound query?
A. It shows products that have a cost recorded irrespective of sales
B. It shows products that were sold and have a cost recorded
C. It shows products that were sold but have no cost recorded
D. It reduces an error
Answer: C
Q:53)
The products table has following structure:
Name NULL DATATYPE
------------------------------------
prod_id Notnull number(4)
prod_name varchar2(25)
prod_expiry_date date
SQL>SELECT PROD_ID,NVL2(PROD_EXPIRY_DATE,PROD_EXPIRY_DATE + 15,'') FROM PRODUCTS;
SQL>SELECT PROD_ID,NVL(PROD_EXPIRY_DATE,PROD_EXPIRY_DATE_15) FROM PRODUCTS;
Which statement is true regarding the outcome?
A. Both the statements execute and give the same result
B. Both the statements execute and give different results
C. Only the second SQL statement executes successfully
D. Only the first SQL statement executes successfully
Answer: B
Q: 54)
Which statements are correct regarding indexes? (Choose all that apply.)
A. For each data manipulation language (DML) operation performed, the corresponding indexes
are automatically updated.
B. A nondeferrable PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE KEY constraint in a table automatically creates a
unique index.
C. A FOREIGN KEY constraint on a column in a table automatically creates a non unique key
D. When a table is dropped, the corresponding indexes are automatically dropped
Answer: A,B,D
Q:55)
Which two SQL statements would execute successfully? (Choose two.)
A.
UPDATE promotions
SET promo_cost = promo_cost+ 100
WHERE TO_CHAR(promo_end_date, 'yyyy') > '2000';
B.
SELECT promo_begin_date
FROM promotions
WHERE TO_CHAR(promo_begin_date,'mon dd yy')='jul 01 98';
C.
UPDATE promotions
SET promo_cost = promo_cost+ 100
WHERE promo_end_date > TO_DATE(SUBSTR('01-JAN-2000',8));
D.
SELECT TO_CHAR(promo_begin_date,'dd/month')
FROM promotions
WHERE promo_begin_date IN (TO_DATE('JUN 01 98'), TO_DATE('JUL 01 98'));
Answer: A,B