Terraform block
Class 19th Terraform block and provide version constraints May 9th(Devops)
Providers block
Local Version changing
Terraform block and provider version constraints
Hcp Cloud
Provider Block
By default, provider plugins in terraform change every few weeks
When we run the init command , it download the latest plugins always.
Some code will not work with old plugins, so we need to update them
To get the latest provider plugins: https://registry.terraform.io/browse/providers.
When you add a new provider,"terraform init" is a must.
terraform providers:Lists the providers required to run the code.
To create infrastricture on any cloud,all we need to have is a provider
Types: Official: Manager by terraform
Partner:Managed by a third-party company
Community:Managed by individuals
For The Terraform Block provider block ,here we need mentioned our provide, forex aws,azure,GCP..etc when you do terraform init ,automatically terraform get the latest plugin's from
the provider, Some time we need mention specific version also, instead of latest version
Ex:-Provider "aws"{
}
Below is the Script for Terrafrom installation on Amazon Linux
sudo yum install -y yum-utils shadow-utils
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/AmazonLinux/hashicorp.repo
sudo yum -y install terraform
Step1: After terraform installation ,we can able give command check version of terraform
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ~]$ terraform --version
Terraform v1.11.4
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ~]$ cat cloudinfra.tf
provider "aws"{
region ="eu-west-1"
}
Step2:While enter the command terrafrom provider plugin's installing
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ~]$ terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding latest version of hashicorp/aws...
- Installing hashicorp/aws v5.97.0...
Step3: As see now terraform version coming with provide version also, the version will be change frequently, we have feasibility to change version whatever your required for you code,
As see below provide screen shot Version 6.0.0-beta version exist but for later terrafrom take 5.97.0 version ,Due to beta mean it is not full-fledged release to market still testing phase, so latest installed 5.97.0 only, if you want give specific version to install your instance ,right of the screen shot,take code and copy, enter terrform init for desired version
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ~]$ terraform --version
Terraform v1.11.4
on linux_amd64
+ provider registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws v5.97.0
Step4:Give the code and save run the command terraform init -upgrade
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ cat cloudinfra.tf
provider "aws"{
region ="eu-west-1"
}
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "6.0.0-beta1"
}
}
}
Step5: As see below terraform upgraded beta version ,we have specifically mentioned the version so that , it was installed you can downgrade also using same command
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ terraform init -upgrade
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding hashicorp/aws versions matching "6.0.0-beta1"...
- Installing hashicorp/aws v6.0.0-beta1...
- Installed hashicorp/aws v6.0.0-beta1 (signed by HashiCorp)
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ terraform -version
Terraform v1.11.4
on linux_amd64
+ provider registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws v6.0.0-beta1
Step6:Downgrade V6.0.0 same command , we can use > lessthan < greater than also using version >="5.96.0"
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ terraform init -upgrade
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding hashicorp/aws versions matching "5.96.0"
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ terraform -version
Terraform v1.11.4
on linux_amd64
+ provider registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws v5.96.0
Provisioners(File, Local-exec, Remote exec)
If you are working with multiple instances file transfer from server provisioner will help
Local-Exec Provisioner ,Remote-Exec Provisioner ,File Provisioner
Local-Exec Provisioner: (Using for logs storage for particular instance)
Runs a command on your local machine (Where terraform is executed)
Useful for tasks like sending notifications or running local scripts
Remote-Exec Provisioner:(if you want execute any commands )
Runs commands on the remote machine after SSH access.
Used for configuration tasks like installing packages
File Provisioner:(if any file created local move remotely for that file using this, it will work ssh protocol)
Transfer files from your local machine to the remote instance
Works only for resources with SSH access (like EC2)
Metadata information about for ex:-s3 create for bucket information ,if want store use local executor
which local executor created the file ,the file if you want to copy any other instance using file executor .
Remote executor terraform code while you creating instance if want run command or installed any package use remote executor
Practical Local executor
Step1: The depends_on argument in Terraform is used to explicitly declare resource dependencies.
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ cat cloudinfra.tf
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-1"
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "bucketlocal"{
bucket ="ccitmay92025"
tags = {
Name ="Dev Bucket"
Environment ="Development"
}
}
resource "null_resource" "save_bucket_details" {
depends_on = [aws_s3_bucket.bucketlocal]
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = <<EOT
echo "Bucket Name: ${aws_s3_bucket.bucketlocal.id}" > bucket_detail.txt
echo "Region: eu-west-1" >> bucket_detail.txt
echo "Tags: Name=${aws_s3_bucket.bucketlocal.tags.Name},Environment=${aws_s3_bucket.bucketlocal.tags.Environment}" >> bucket_detail.txt
EOT
}
}
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ terraform apply -auto-approve
Apply complete! Resources: 2 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Step2: as you see below bucket details capture as ouput
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ ls -lrt
total 12
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 617 May 10 13:41 cloudinfra.tf
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 90 May 10 13:43 bucket_detail.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 3266 May 10 13:43 terraform.tfstate
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ cat bucket_detail.txt
Bucket Name: ccitmay92025
Region: eu-west-1
Tags: Name=Dev Bucket,Environment=Development
Bucket created successfully
Transfer the file from one instance to other instance you need sshkey .pem file for the source instance to destination instance sshkey copy this server to connect target server
Step1:Actually we are using same pem file to connect any other linux server ,similay way you can
give same .pem fie key to which you going create the target server key also
Step2: Source instance ~/.ssh/ this path create file copy above key and save
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 .ssh]$ pwd
/home/ec2-user/.ssh
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 .ssh]$ vi my-key.pem
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 .ssh]$ ls -lrt
total 8
-rw-------. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 391 May 10 11:56 authorized_keys
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 1679 May 10 14:23 my-key.pem
Step3:
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-137 ccit]$ cat cloudinfra.tf
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-1"
}
# Create an EC2 Instance (Amazon Linux 2)
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-04e7764922e1e3a57" # Amazon Linux 2 AMI
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "Terraform" # Replace with your SSH key
subnet_id = "subnet-0477e85088645156b"
# Step 1: Create a local file with instance details
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = <<EOT
echo "Instance ID: ${self.id}" > instance_details.txt
echo "Public IP: ${self.public_ip}" >> instance_details.txt
echo "Region: ap-south-2" >> instance_details.txt
EOT
}
# Step 2: Copy the file to the EC2 instance
provisioner "file" {
source = "instance_details.txt"
destination = "/home/ec2-user/instance_details.txt"
}
connection {
type = "ssh"
user = "ec2-user"
private_key = file("~/.ssh/my-key.pem") # Path to your private key
host = self.public_ip
}
}
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-0-213 ccit]$ terraform apply -auto-approve
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-137 ccit]$ ls -lrt
total 20
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 970 May 10 19:35 cloudinfra.tf
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 76 May 10 19:36 instance_details.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 181 May 10 19:36 terraform.tfstate.backup
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 4723 May 10 19:36 terraform.tfstate
Step3: New instance created successfully.
Step4: Need to check file transferred or not you see target side file transferred successfully
Source:
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-137 ccit]$ cat instance_details.txt
Instance ID: i-02cd51ac159fe6169
Public IP: 54.73.41.102
Region: ap-south-2
Target file transferred successfully
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-171 ~]$ ls -lrt
total 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 76 May 10 19:36 instance_details.txt
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-171 ~]$ cat instance_details.txt
Instance ID: i-02cd51ac159fe6169
Public IP: 54.73.41.102
Region: ap-south-2
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-137 ccit]$ terraform destroy -auto-approve
Destroy complete! Resources: 1 destroyed.
Remote executor
Packages and User command installed while launching the instance inline query we have mentioned the query ,all command installed remotely
Step1
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-137 ccit]$ cat cloudinfra.tf
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-1"
}
# Create an EC2 Instance (Amazon Linux 2)
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-04e7764922e1e3a57" # Amazon Linux 2 AMI
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "Terraform" # Replace with your SSH key
subnet_id = "subnet-0477e85088645156b"
# Step 1: Create a local file with instance details
tags = {
Name = "CCIT-Website"
Environment = "Production"
}
# Execute commands inside EC2
provisioner "remote-exec" {
inline = [
"#!/bin/bash",
"sudo yum update -y",
"sudo yum install -y httpd git",
"sudo systemctl start httpd",
"sudo systemctl enable httpd",
"git clone https://github.com/cloudcomputingintelugu/ccitwebsite.git",
"sudo cp -r ccitwebsite/* /var/www/html/",
"sudo chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html",
"sudo systemctl restart httpd"
]
}
connection {
type = "ssh"
user = "ec2-user"
private_key = file("~/.ssh/my-key.pem") # Path to your private key
host = self.public_ip
}
}
output "website_url" {
value = "http://${aws_instance.example.public_ip}"
}
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-137 ccit]$ terraform apply -auto-approve
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
website_url = "http://3.250.69.211"
Instance created successfully and installed Apache and also host the website
As you see new instance wesite file stored run time
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-182 ccitwebsite]$ pwd
/home/ec2-user/ccitwebsite
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-182 ccitwebsite]$ ls -lrt
total 44
-rw-rw-r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 789 May 10 21:15 readme.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 ec2-user ec2-user 40878 May 10 21:15 index.html
drwxrwxr-x. 8 ec2-user ec2-user 77 May 10 21:15 assets
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-182 ccitwebsite]$
[ec2-user@ip-10-0-3-137 ccit]$ terraform destroy -auto-approve
Destroy complete! Resources: 1 destroyed.
- HCP Cloud introduction and features
- Github communication
- Build Infra with HCP
Hashicorp Cloud , We need signup the account in HCP cloud and link to Git hub files
and build the infrastructure
HCP Cloud Introduction and features
Hcp means HashiCorp cloud platform
it is a managed plant form to automate cloud infrastructure
it provides privacy,security and isolation
it supports multiple providers like AWS,Azure and Google cloud
It offers a suite of open-source tool for managing infrastructure,including terraform,vault,consul, and Nomad.
we can use different code repositories for a project
we can use variable sets to apply the same variables to all the workspaces.
Step1:
- Go to Google & type: Hcp cloud account sing-in/Signup
- Email & password
- Continue with HCP account
- Create A Git hug account
- Create repo-->name -->add new file -->write terraform code -->commit
https://www.hashicorp.com/en/cloud
here is benefits of HCP cloud terraform state file automatically handled by HCP cloud , if any one multiple people working same repository it is locked automatically we need unlock manually,
if any done in git commit automatically terraform plan applied to HCP infra side , need apply manually
HCP Service: Vault,consul,Boundary,waypoint,terraform ..etc
While login automatically Created project vakati-subbu-org
Main products
- Terraform: to create infrastructure
- Vault to manage the secrets and protecting sensitive data
- Normad: to schedule,deploy and manage applications
- Consul: to secure serive-to-service communication and networking
- Packer:to create images for launching servers
Step2:Select Terraform click -> continue to HCP Terraform -->Click Continue with Hcp account
Create a new HCP-linked account ->Click continue
Create organization name click create organization
Step3: Now need linkup and git hub repository ,as you see below version controls in HCP, aws has earlier version control code commit now not supported
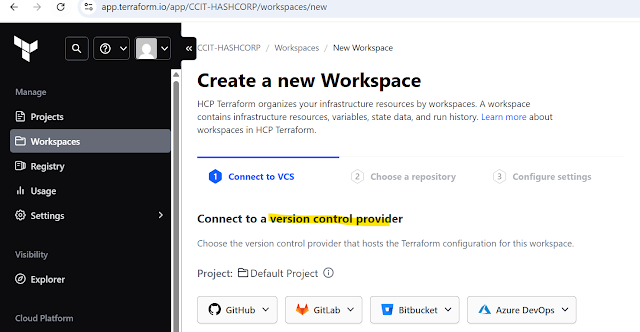
Click GitHub >Github.com >Signin git >approved authorized terraform cloud click continue
See below all your repositories are showing in HCP cloud
Git Create new repository
Refresh the HCP Cloud select the repository >it will create the new Workspace
$ git clone https://github.com/Vakatisubbu/ccitterrfrom.git
$git add .
$git commit -m "First commit"
$git remote add origin https://github.com/Vakatisubbu/ccitterrfrom.git
$ git push -u origin main
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 336 bytes | 336.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
To github.com:Vakatisubbu/ccitterrfrom.git
6e92495..79ce011 main -> main
branch 'main' set up to track 'origin/main'.
Signin Git with token instead of username and password
Git >setting >Developer Settings >personal access tokens >fine-grained tokens >click Geneate new token >give tokenname "ccitgittoken" >select all repositories >click generate token
it temporary only 7 days like that
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
sign in with next time with token
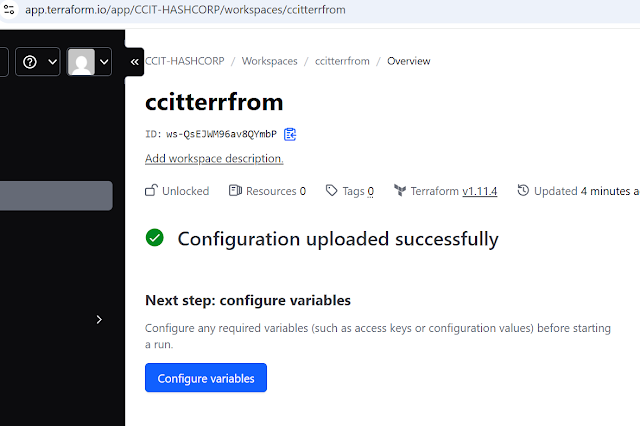
This Our new workspace ,here configure variables
Click configure variables, for setup the environmental variables HSCP to communicate AWS
need to provide secrete key and authentication ,take any user Authentication detail in AWS side
AWS >IAM USER > admin user it has already administrator access, select Security credentials
>Accesskey >Click Create access key
click next ,click Create access key, download file click done
Access like below ,We need follow some structure environment key set should follow the same
Access key ID Secret access key
AKIATFBMO7H4GQ5PHUZS p0XMp+d7h2xPrPm3UsIB6BO/2clP7S+7I40LvSV3
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID =
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY =
check box check sensitive for security ,add another variable same , next click new run
Click New run and then click start
Step 4: I have done small change on the git and commit , HCP planning is running automatically
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ vi Cloudinfra.tf
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ git add .
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ git commit -m "third commit"
[main 0432933] third commit
1 file changed, 4 insertions(+), 3 deletions(-)
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ git push -u origin main
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 333 bytes | 166.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
To github.com:Vakatisubbu/ccitterrfrom.git
ead2ea9..0432933 main -> main
branch 'main' set up to track 'origin/main'.
HCP planning is running automatically
As see below plan finished successfully
You need to Apply manualy,click give comments "First bucket creation HCP" and then confirm apply

$ cat Cloudinfra.tf
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-1"
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "ccitbucket" {
bucket = "ccitapril"
}
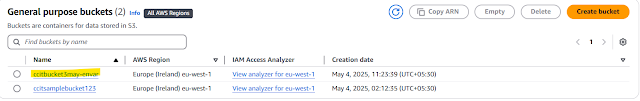
AWS console bucket created
Added second Bucket HCP colud automatically planned, you need apply manually
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ cat Cloudinfra.tf
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-1"
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "ccitbucket" {
bucket = "ccitapril"
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "ccitbucket1" {
bucket = "ccitaprilmay"
}
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ git add .
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ git commit -m "Second Bucket creation"
[main b109ec8] Second Bucket creation
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
Administrator@DESKTOP-AV2PARO MINGW64 /c/git_repos/ccitterrfrom (main)
$ git push -u origin main
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done.
Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 284 bytes | 284.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1), completed with 1 local object.
To github.com:Vakatisubbu/ccitterrfrom.git
8c49066..b109ec8 main -> main
branch 'main' set up to track 'origin/main'.

Aws console Second bucket created.
Destroy plan
HCP Setting >Destruction and deletion >click button Queue destroy plan ,give name Queuedestroyplan
Three bucket Destroyed plan ready and confirm through HCP
in aws console also S3 bucket removed successfully.
--Thanks